Supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No.: 91956000, 22031006, 21861132003), the research team led by Luo Sanzhong from Tsinghua University has developed a ground-breaking method for chiral synthesis. The research was published in science on February 25, 2022, entitled "deracemization through photochemical E/Z isomerization of enamine". The article link is http://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.abl4922.
Facile access to single mirror-image isomer or enantiomer of a molecule remains a central task in chemical synthesis that has significant relevance in pharmaceutical industry and biological science. One of the long-sought ideal pathway is to directly convert a racemate, mixtures of enantiomers, into a single enantiomer with 100% yield. This process is called deracemization (Fig. a). However, such a pathway is endergonic and is also kinetically against microscopic principle. To break the thermodynamic and kinetic constraints remain a great challenge in chiral synthesis.
The team of Luo Sanzhong has previously developed the first asymmetric protonation of enamine (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 11451-11455) by using their bio-inspired chiral primary amine catalyst. On this basis, the team has developed an elegant solution to the challenging deracemization of aldehydes by combining enamine protonation and photocatalysis (Fig. b). Photochemical equilibrium could be achieved within 1 hour to achieve efficient deracemization under mild conditions. The reaction demonstrated broad scopes, tolerating electron withdrawing groups, electron donating group, alkyl group, polar functional group as well as heterocycles. The current protocol can be up-scaled and successfully applied in the synthesis of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. The key to success is found to be the photochemical E/Z isomerization of enamine intermediate (Fig. c). This research not only provides a new approach for chiral synthesis, but also sheds new lights for the development of asymmetric organocatalysis.
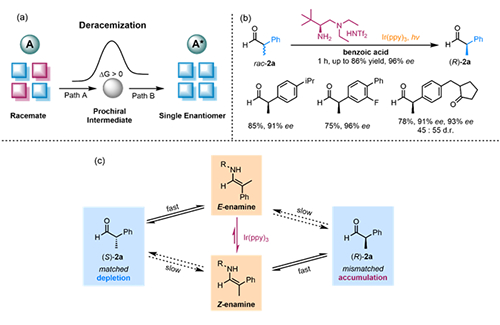
Figure (a) Illustration of deracemization;(b) selected results on the developed deracemization process;(c) reaction mechanism

Add: 83 Shuangqing Rd., Haidian District, Beijing, China
Postcode: 100085
Tel: 86-10-62327001
Fax: 86-10-62327004
E-mail: bic@donnasnhdiary.org
京ICP备05002826号 文保网安备1101080035号 Copyright 2017 NSFC, All Right Reserved