Supported by NSFC (52076127), an interdisciplinary research team led by Prof. Xiaoshi Qian at Shanghai Jiao Tong University published the research article, "High-entropy polymer produces giant electric heating effect in low field", in Nature on Dec. 22, 2021 (http://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-021-04189-5/). It is the first time that a Chinese scientific research institute published a paper about electrocaloric materials in Nature.
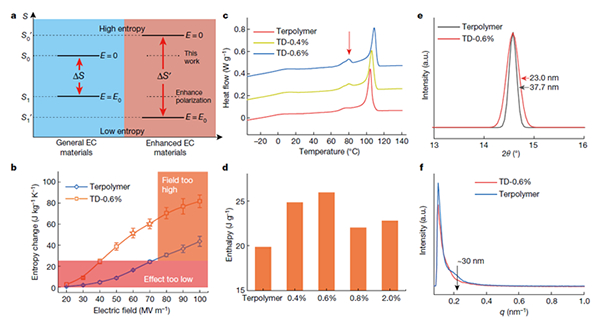
Figure1 Low-field ECE enhancement by designing a high-entropy material.
The electrocaloric effect is an intriguing physical phenomenon of dielectrics, in which a material shows a reversible temperature change under an applied electric field. Electrocaloric refrigeration technology utilizes solid refrigerant, which has zero greenhouse effect, high energy efficiency (COP), easy to miniaturization and being lightweight. It is one of the disruptive innovations that could contribute to China’s Dual-Carbon goal. However, the currently state-of-the-art dielectrics for cooling still require an extremely high electric field to produce an industrially usable cooling effect, which would cause the aging and breakdown of materials under the working condition. Therefore, the improvement of the electric-field-induced entropy change in dielectrics under is a research direction of great significance, especially under low fields.
This work designed of high-entropy polymers to increase the entropy change (increase the zero-field entropy) by facilely controlling the molecular defects. Driven by the same external electric field (50 MVm-1), the electric-field-induced-entropy change in this polarized high-entropy material is nearly 4 times that of the current the-state-of-the-art refrigerant polymer. Multiple structural analysis demonstrated that the crystallinity of the high-entropy polymer increases, meanwhile, its crystal size reduces. The results indicated that the polar entities were significantly increased. Therefore, degree of freedom and polar entropy in the material are significantly increased.
The high-entropy EC polymer exhibit large ECE that surpassed the threshold of the industrial demand under merely 40 MVm-1. The giant ECE exhibits an elongated lifetime to over one million cycles. After one million cycling process, the cooling effect reduced less than 10%, and the hysteresis heat was reduced as well. The device level simulation suggested that the solid-state refrigerator adopting these high-entropy polymers show the largest temperature span over 50 K, and thermodynamic perfection over 80% under 20 K temperature span.

Add: 83 Shuangqing Rd., Haidian District, Beijing, China
Postcode: 100085
Tel: 86-10-62327001
Fax: 86-10-62327004
E-mail: bic@donnasnhdiary.org
京ICP备05002826号 文保网安备1101080035号 Copyright 2017 NSFC, All Right Reserved