With the support of NSFC-ISF(China-Israel) collaborative project (Ministry of Science No.: 3201101152, approval No.: 32061143028), Professor Su Bing's group from School of Medicine , Shanghai Jiao Tong University discovered and named a new type of intestinal stromal cell called MRISC that exists underneath the intestinal stem cell, which reveals the significance of MRISC in resolving the intestinal epithelial injury upon intestinal inflammation and damage and provides novel insights for the clinical treatment of colitis associated diseases. The related studies have been published online in Nature on March 3, 2021 with the title of "Map3k2-regulated intestinal stromal cells define a distinct stem cell niche". Link to the paper: http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-03283-y .
Intestinal stromal cells are important members of intestinal microenvironment. Different groups of intestinal stromal cells participate in maintaining the integrity of epithelial structure by secreting growth factors and cytokines, which can effectively regulate intestinal homeostasis. However, under the condition of intestinal homeostasis and disease, it is still unclear how different intestinal stromal cell populations regulate the intestinal function. Little is known about the characteristics and spatial distribution of different intestinal stromal cell subsets, as well as their regulatory functions, cellular and molecular mechanisms in tissue injury repair.
Map3k2, an evolutionarily conserved serine / threonine protein kinase, is constitutively expressed in human and mouse organs. Dr. Su Bing’s group first finds that Map3k2 can protect mice from DSS induced enteritis by maintaining the number and function of damaged intestinal Lgr5 + stem cells. This study finds that Map3k2 up-regulates the expression of Wnt activator R-spondin1 in response to DSS induced injury, mediates the interaction between MAPK signal and Wnt signal, and confirms that intestinal stromal cells are the key cells for up-regulating the expression of R-spondin1 in intestinal inflammation. In this study, researchers isolate intestinal stromal cells (MRISC) with the characteristics of CD90 + CD81 + CD34 + CD138 - and successfully prove that MRISC is located in the "stem cell niche" in the intestine and plays a specific regulatory function on intestinal stem cells.
This study further finds that MRISC has special epigenetic regulatory characteristics compared with other stromal cells, and finds a novel molecular pathway of "reactive oxygen species (ROS) - Map3k2-ERK5-Klf2" to induce the production of R-spondin1. By the comparative analysis of human intestinal single cell sequencing data, this study also finds the corresponding human intestinal MRISC.
This research is significant for the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease targeting the epithelial stem cell microenvironment. At the same time, the newly established interstitial cell tracing model will greatly promote the development of the research field of intestinal microenvironment. The establishment of MRISC and the labeling system of stromal cell subsets will greatly promote the functional interpretation of stromal cells in multiple fields of life science research, such as immunology, neuroscience, tumor biology, metabolism and aging. The identification of stromal cell subsets in human body will also elucidate the role of stromal cells in human inflammation related diseases.
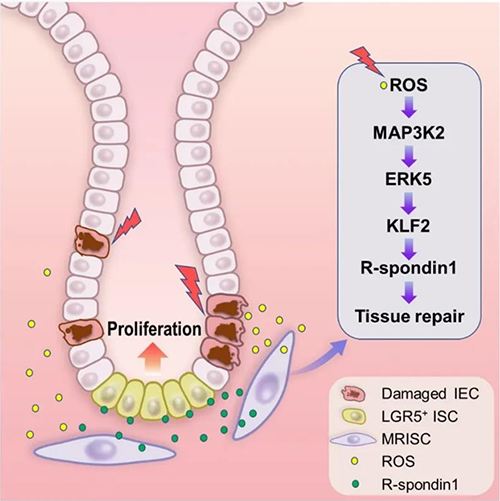
Fig.1 the model of MRISC function

Add: 83 Shuangqing Rd., Haidian District, Beijing, China
Postcode: 100085
Tel: 86-10-62327001
Fax: 86-10-62327004
E-mail: bic@donnasnhdiary.org
京ICP备05002826号 文保网安备1101080035号 Copyright 2017 NSFC, All Right Reserved