Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 71704156), the collaboration between Professor Jianxing Yu, Assistant Professor Yongdong Shen, Assistant Professor Biao Huang from Zhejiang University and Assistant Professor Yuan Cheng from University of Minnesota, has achieved new progress in the research area of government and non-profit cooperation. This study, titled Coproducing Responses to COVID-19 with Community-Based Organizations: Lessons from Zhejiang Province, China, has been published in Public Administration Review on May 26, 2020 (http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/puar.13244).
After the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic, China has put in place strong wartime-like measures and kept the virus in control in a rapid manner. Despite such a huge success in containing COVID-19, China is confronting mixed feelings and comments from the rest of the world, especially developed countries in Europe and North America. Surprised by the achievement China’s made in such a high population density, they falsely associate the success of China to the complete lockdown in Wuhan and the extreme power of the state machinery The research evaluated for the first time how community-based organizations worked with their local governments to coproduce responses to COVID-19, and pointed out that the active participation of all social members is one of the key factors for China’s success in containing the COVID-19 pandemic. The research contributes a new insight to the response to COVID-19 with a perfect example of why coproduction and community-based solutions are important. It highlights the crucial roles of the local governments, community-based organizations and common citizens have played in different stages of the COVID-19 response.
The results found in Zhejiang show that citizen coproduction and the involvement of community-based organizations are of vital significance to the social and economic recovery, and the emerging digital technologies have further strengthened the networking between local governments, community-based organizations and citizens. The major roles of community-based organizations during COVID-19 included mobilizing volunteers to trace the source and spread of COVID-19, collecting donations and supplies for epidemic control, providing necessary social and community services, offering welfare services, assisting enterprises with production resumption, exerting psychological counselling and social work, and building collaboration platforms to promote sustainable economic development.
As the COVID-19 pandemic continues in such a globalized world, how can public sector leaders in other localities and countries learn from Zhejiang’s experience? We propose the following recommendations for public sector leaders to better engage their citizens and community-based organizations in their responses to COVID-19.
· Strategically engaging community-based organizations in coproducing responses to COVID-19 is crucial for emergency management and post-crisis recovery.
· Incentivizing Volunteers to Participate in the Prevention and Control of COVID-19.
· Setting up the data and institutional infrastructure to facilitate the participation of their citizens and community-based organization in crisis management and response.
· Building Trust and the Long-Term Capacity of Community-based organizations
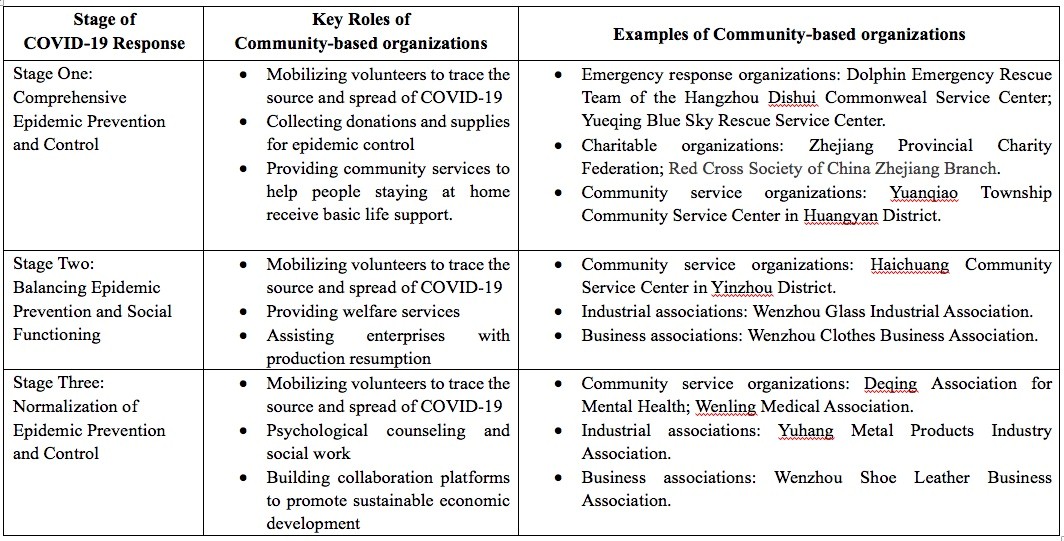
Table. The Critical Roles of Community-based organizations in China’s Responses to COVID-19

Add: 83 Shuangqing Rd., Haidian District, Beijing, China
Postcode: 100085
Tel: 86-10-62327001
Fax: 86-10-62327004
E-mail: bic@donnasnhdiary.org
京ICP备05002826号 文保网安备1101080035号 Copyright 2017 NSFC, All Right Reserved