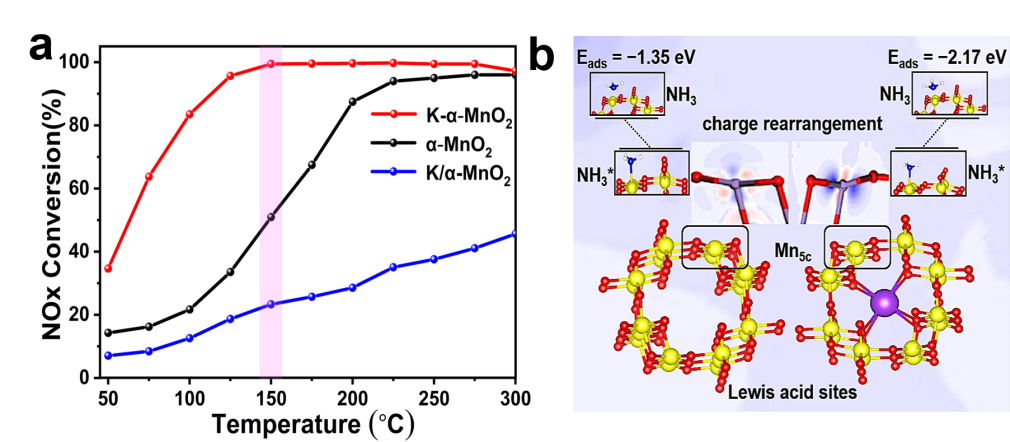
Fig. 1 Catalytic activity and mechanism of potassium ions
inserted α-MnO2 in NH3-SCR
With the support of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21722702, 21872102), Professor Sihui Zhan’s team from the College of Environmental Science and Engineering of Nankai University in China have made important progress in the study of interface chemistry for environmental pollution control. The research has been published in Angewandte Chemie International Edition with the title of “The Role of Alkali Metal in α-MnO2 Catalyzed Ammonia-Selective Catalysis” on March 18th, 2019 ( http://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201901771).
Ammonia selective catalytic reduction (NH3-SCR) is one of the most widely used and efficient technology for the abatement of NOx from the exhausts of stationary and mobile sources. However, alkali metal ions in the stack gases are easy to react with the active sites of the catalyst and to change their chemical structure, which can lead to severe deactivation of such SCR catalysts.
In the process of overcoming this fundamental flaw, Zhan’s team at Nankai University discovers an unexpected phenomenon that the incorporation of K+ in the tunnels of α-MnO2 can greatly improve the catalytic activity at low temperature. Results show that K+ in the tunnels could form a stable coordination with eight nearby Osp3 atoms. The columbic interaction between the trapped K+ and O atoms can rearrange the charge population of nearby Mn and O atoms, making the topmost five-coordinated unsaturated Mn cations (Mn5c, the Lewis acid sites) more positive. Therefore, the more positively charged Mn5c can better chemically adsorb and activate the NH3, which can greatly improve low-temperature performance in the NH3 selective catalytic reduction.
This research achievement not only provides an effective strategy to improve the reaction activity of the catalyst, but also demonstrates the relationship between active sites and catalytic activity at the atomic level, which is an interesting case for applying interface chemistry in the field of environmental pollution control.

Add: 83 Shuangqing Rd., Haidian District, Beijing, China
Postcode: 100085
Tel: 86-10-62327001
Fax: 86-10-62327004
E-mail: bic@donnasnhdiary.org
京ICP备05002826号 文保网安备1101080035号 Copyright 2017 NSFC, All Right Reserved